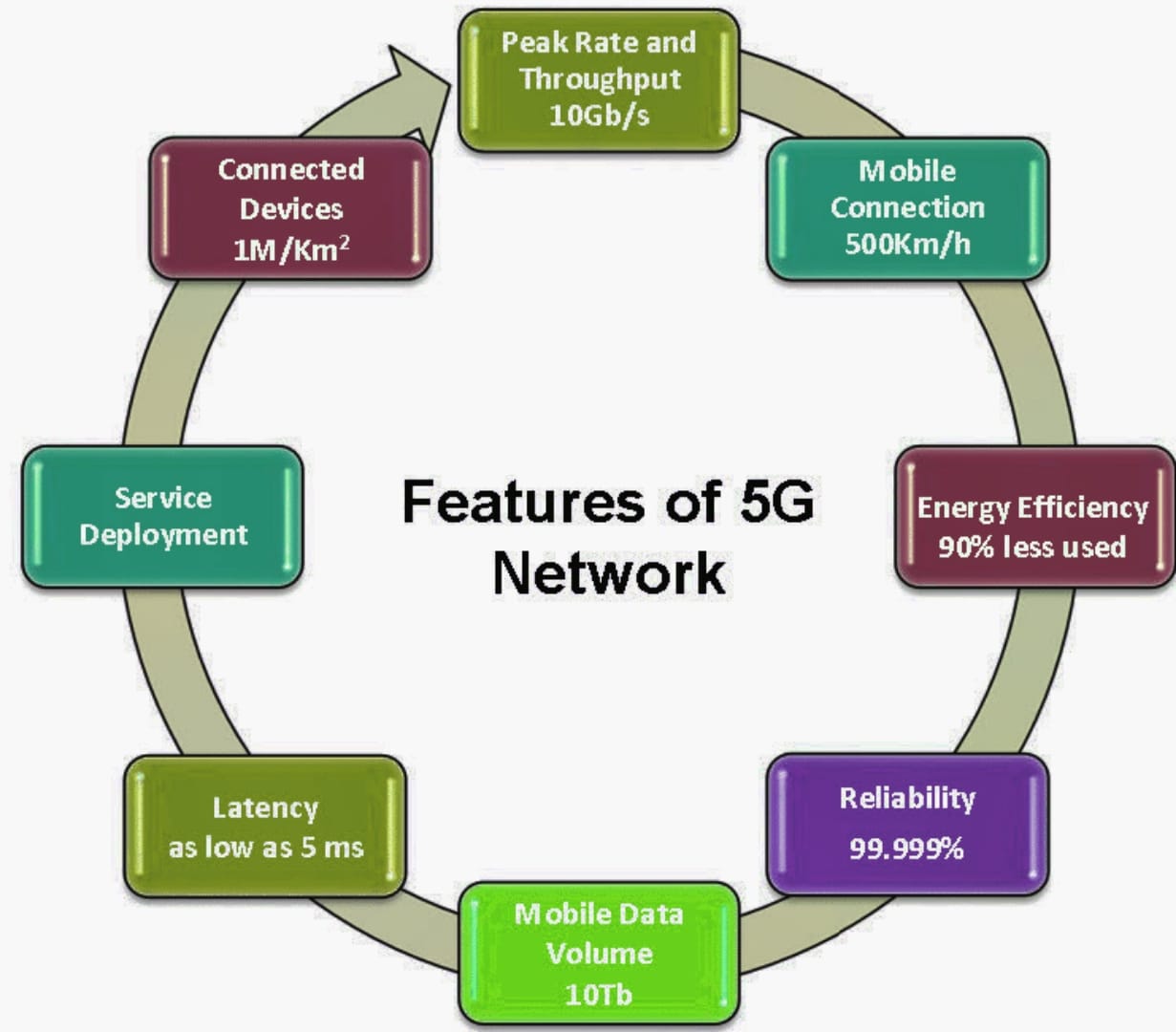
Introduction
The world is rapidly moving into a digital era with speed, efficiency, and connectivity. It is undoubtedly that among the most significant advancements of recent years is the rollout of 5G technology. Though most of us have heard of the 5G technologies, usually some confusion remains of what and how it differs from other generations and the challenges it presents.
In this detailed blog post, we will look at both the benefits and challenges of Ag technology. Real-world examples, insights from various experts, and case studies have been incorporated with a bulky technique to help understand how 5G is driving the world forward. This guide is intended for techies, business owners, and those who tend to draw a blank about 5G Watch out for what you need to know about 5G together where useful.
From 1G to 5G: An Evolutionary History of Wireless Networks
Before diving in, let’s see how things got to such a point. The 1G to 5G timeline spans a few decades, and each generation brings significant improvements.
1G (1980s) – First-generation network: Introduced analog voice communication, with terribly slow connectivity and started poor voice quality.
2G (1990s) – Digital voice transmission provided decent call quality, with the SMS (text messaging) feature being added.
3G (2000s) – Mobile internet was born, paving the way for smartphones.
4G (2010s) – High-speed internet provides HD video streaming and efficient use of apps.
5G (2020s and beyond) – Directs ultra-fast data speeds that have low latencies and gigantic connectivity to machine-type communication IoT devices.
The 5G Promise: Benefits That Count
- Speed and Low-Latency
One of the biggest advantages of 5G is the sheer speed. By contrast, 4G affords average download speeds of 10-50 Mbps, providing under ideal conditions download speeds of as much as 10 Gbps. With this fact, it will be approximately flawless to download big-sized files, stream in ultra-high-definition and play cloud games in real-time. Besides, with a latency of only one millisecond into the market, 5G will enhance applications that require instant response, such as driving automatic and remote surgeries.
Imagine a world in which doctors perform remote robotic surgeries over 5G – a feat only achievable through almost instantaneous response times offered by 5G.
- Enhanced Connectivity for IoT Devices
5G is set to reveal a new paradigm of device-to-device communication in the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape. Smart homes and smart cities to industrial automation will all need a network to keep billions of devices connected without delays. For instance, in a smart city, traffic management would be optimized through 5G by linking cars and traffic lights with road sensors to reduce jams and augment road safety.
The example comes from South Korea, with AI-based traffic management systems enabled by 5G managing city traffic and bringing down congestion levels by 25 percent in some of the major cities.
- Enhanced Ability to Work and Study from Home
With more people working and studying remotely, fast and reliable internet access has never been more important. This will provide high-speed video conferencing and collaboration support for virtual teamwork and cloud applications that enable better remote work and learning. Imagine a rural-area student being able to attend high-quality virtual lectures without buffering, something hence made possible through 5G.
Experts believe that 5G will create an equal platform to have broadband access for same-speed internet in less privileged areas – this helps empower students and workers alike.
- Transforming Healthcare
The healthcare sector is already feeling the impact of 5G in telemedicine, remote monitoring, and, indeed, robotic surgery. It becomes easier for hospitals to send large medical images instantaneously, leading doctors to examine patients fast. Further, there are wearables connected to 5G networks, allowing for real-time surveillance of patient health, which is particularly important for older patients and chronic patients.
China, for instance, has operated remote surgeries using 5G technology successfully, hinting the potential it holds for completely changing healthcare access.
The Watsony World of 5G: Considerations for Obstacles
- High Cost of Infrastructure
The 5G network rollout calls for the spending of massive funds on infrastructural development for establishing new cell towers, fiber optics, and adequate network equipment. Unlike 4G that employs larger cell towers dispersed far from each other, 5G further calls for small cell towers dispersed really close to each other, adding to the total cost of deployment.
Verizon and AT&T are investing billions in setting up a 5G network, but these expenses may delay widespread adoption anywhere, especially in developing countries.
- Absence of 5G Coverage for Rural Areas
While 5G is fast penetrating urban areas, rural areas still face an uphill struggle with regards to coverage. The challenges of establishing 5G networks in remote locations is attributed to the requirement for closely-spaced cell towers, which makes it difficult to set up these networks. This digital divide may only exacerbate inequalities between urban and rural communities in terms of technology access.
Limited infrastructure for fiber in some parts of Africa and India, for example, has been an obstacle to 5G adoption, leading many areas to remain dependent on older networks.
- Possible Health and Security Issues
Although there is also a dearth of scientific evidence linking 5G to health concerns, a number of communities have expressed concerns about radiation arising from a higher concentration of antennas. In addition, 5G is particularly vulnerable to cybersecurity threats due to relying on software-defined networks and IoT devices. Exploiting these vulnerabilities, hackers can break their way into the expansioning connected systems and cause data breaches that hamper information privacy.
Cybersecurity firms already are creating better encryption protocols to protect user privacy.
- Issues with Device Compatibility
Some devices are not ready to be upgraded to 5G, and the cost of upgrading smartphones, tablets, and routers to be compatible with early 5G technology can be exorbitant for the average consumer and lead to a slowdown in the service. Besides, those companies that rely on legacy systems may find themselves in a position competitively disadvantaged against developments toward the adoption of 5G without incurring significant costs.
A latest study revealed that up to 40% of consumers balk at switching to 5G on account of the expense involved in upgrading devices.
The global implications of 5G
Countries such as China and South Korea are among the first to launch into 5G, with a great deal of research and investigation funding on these topics. Services expected to benefit enormously from smoother operations, factories, and furtherance in technologies concerning AI-based applications. However, more still needs to be done by regulators and government to ensure a fair distribution of data access and right to privacy throughout its growth.
Conclusion: The Future of 5G
5G is destined to disrupt industries and general existence in ways we are just starting to fathom. The sheer extent of transforming healthcare, developing smart cities, and many more will leave one in awe at the dynamism herewith. However, facing the infrastructure costs, rural coverage voids, among many others linked to security, are crucial towards 5G taking off as intended.
Moving forward, a connected world will be envisaged around a cooperative effort of governments, telecom agencies, and technological innovators with these obstacles kept away. As a consumer, a small business owner, or a policymaker, it is crucial to understand 5G, both good and bad, as we move towards a connected future.
This promise of 5G should be taken on board but treated with care and considerations such that this excellent technology serves as a tool for progress rather than division.